Preparing financial statements can seem intimidating, but it doesn’t have to be an overwhelming process. We’ve broken down the steps for preparing an income statement, as well as some helpful tips. Net income—or loss—is what is left over after all revenues and expenses have been accounted for. If there is a positive sum (revenue was greater than expenses), it’s referred to as net income. If there’s a negative sum (expenses were greater than revenue during that period), then it’s referred to as net loss.
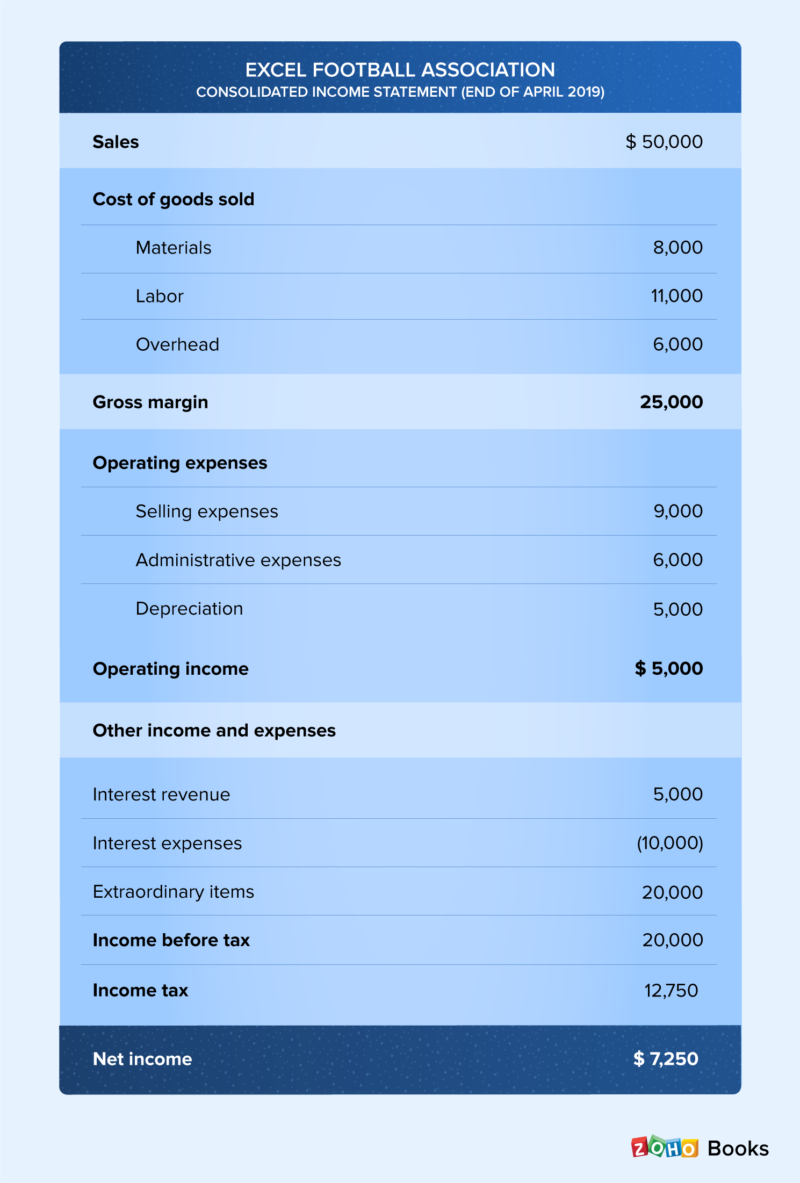
A line-by-line analysis of an income statement
It provides valuable insights into various aspects of a business, including its overall profitability and earnings per share. The multi-step income statement provides an in-depth analysis of the financial performance of a business in a specific reporting period by using these profitability metrics. The single-step format is useful for getting a snapshot of your company’s profitability, and not much else, which is why it’s not as common as the multi-step income statement. But if you’re looking for a super simple financial report to calculate your company’s financial performance, single-step is the way to go.
What is the difference between an income statement and a balance sheet?
Creditors are often more concerned about a company’s future cash flows than its past profitability. However, their research analysts can use an income statement to compare year-on-year and quarter-on-quarter performance. They can infer, for example, whether a company’s efforts at reducing the cost of sales helped it improve profits over time, or whether management kept tabs on operating expenses without compromising on profitability. Include certain amounts that are already required to be disclosed under current GAAP in the same disclosure as the other disaggregation requirements.3. Disclose a qualitative description of the amounts remaining in relevant expense captions that are not separately disaggregated quantitatively.4. Disclose the total amount of selling expenses and, in annual reporting periods, an entity’s definition of selling expenses.
Is EBITDA included in an income statement?
As we saw, while a single-step income statement is straightforward and easy to understand, a multi-step could pose significant challenges, especially if you’re just starting out in accounting. By taking our course Fundamentals of Financial Reporting you’ll be ready to tackle these and most other accounting scenarios you’re likely to encounter in your practice. The income statement/income tax return, balance sheet, and Cash Flow statements are usually used for different purposes.
No, all of our programs are 100 percent online, and available to participants regardless of their location. Our platform features short, highly produced videos of HBS faculty and guest business experts, interactive graphs and exercises, cold calls to keep you engaged, and opportunities to contribute to a vibrant online community. Harvard Business School Online’s Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible.
- The customer may be given a 30-day payment window due to his excellent credit and reputation, allowing until Oct. 28 to make the payment, which is when the receipts are accounted for.
- As you can see at the top, the reporting period is for the year that ended on Sept. 28, 2019.
- This information is presented for a reporting period, which is typically for one month, one quarter, or one year.
- For small businesses with few income streams, you might generate single-step income statements on a regular basis and a multi-step income statement annually.
Where appropriate, the firm should provide a footnote to explain the nature of the gain or loss. The fact that the survey showed 204 disclosures of extraordinary items in 2018 illustrates the restrictive impact of APBO 30 on practice. For example, the disclosure stocksfortots requirements of the opinion would apply if a conglomerate disposes of a glass manufacturing division when it has no other division engaged in that activity. The following example illustrates the reporting of an unusual gain expected to recur.

It shows the company’s revenues and expenses during a particular period, which can be selected according to the company’s needs. A P&L, which stands for profit and loss, indicates how the revenues are transformed into net profit. There are two ways of preparing P&L single step and multi step income statement. Single step gives you the revenue, expenses and the profit or loss of the business while Multi step breaks down operating revenues and operating expenses versus non-operating revenues and non-operating expenses. The income statement is also known as the statement of operations, profit and loss statement, and statement of earnings.
You can know where to cut expenses that aren’t necessary or how to boost revenue streams. For instance, expenses can be delayed or revenue recognised earlier and the appearance of profitability changed. For a company like Tech Grow, these statements drive the decisions on scaling and R&D investment and on managing funds to promote long-term growth. Running a cosy local café or a massive tech company, every business has its own financial needs and goals, and exactly how they execute will differ.
Gross profit is what’s left of your revenue after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS)—the direct costs related to producing goods or providing services. Gains are the earnings produced outside of the sale of your main goods or services. Accurate records of expenses, revenues, and credits are required for tax purposes and can help keep you in compliance with tax regulations. Financial institutions or lenders demand the income statement of a company before they release any loan or credit to the business.

